What is RDP?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a protocol developed by Microsoft, providing the user access to remotely connect with another computer. Microsoft’s remote desktop protocol is the best one available in the market that works efficiently with an effortless graphical user interface (GUI). It can be used between multiple Windows Operating Systems and Devices. In this article we’re going to discuss RDP security and the current RDP vulnerabilities.
How RDP Works:
Let's make it a bit easier to understand by explaining it with an example. Consider you have a toy car that is controlled by a remote, when you steer the car using the remote you are passing instructions down to the car from the remote. Similarly, when you are granted access to another computer with RDP protocol, you can view the display of the computer and can pass instructions to it from your mouse or keyboard over the internet. This thus provides you access to control the computer with a little hustle.
Vulnerabilities in RDP:
We’re going to go over the most recent RDP security measures and RDP vulnerabilities that are the most commonly heard of.
Windows Remote Desktop Protocol Security Feature Bypass
Released: Jul 11, 2023 Windows RDP Security Feature Bypass (CVE-2023-35332) The core of the issue lies in the utilization of an obsolete and deprecated protocol, Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) version 1.0, posing substantial security and compliance risks to organizations. If an attacker can achieve a machine-in-the-middle (MitM) position and successfully exploit this weakness, they could compromise the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted when the targeted user connects to a trusted server.
Employing outdated and deprecated security protocols, like DTLS 1.0, can result in unintentional non-compliance with crucial industry standards and regulations such as FEDRAMP, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and more. Numerous organizations may unknowingly find themselves in violation of their compliance obligations due to this concern.
Windows Remote Desktop Security Feature Bypass
Released: Jul 11, 2023 Windows RDP Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2023-32043). If a malicious actor manages to establish a machine-in-the-middle (MitM) position and exploit this vulnerability, they could circumvent the certificate validation process that occurs when a targeted user connects to a trusted server.
Windows Remote Desktop Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Released: Jul 11, 2023 Windows RDP Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2023-35352). In the event of a successful exploitation of this vulnerability, an attacker could evade certificate or private key authentication while establishing a remote desktop protocol session.
BlueKeep (Remote Code Execution Vulnerability):
BlueKeep is one of the most drastic vulnerabilities in RDP (Microsoft Vulnerability Protocol Code: CVE-2019-0708). This vulnerability allows the attackers to execute any code they want if they hit the right port, which is most probably port: 3389. BlueKeep is also wormable (it is viable to spread to all the computers within the same network), without any actions performed by the user.
CVE-2022-21893 discovered in January 2022 this vulnerability enables any standard unprivileged user to connect to a malicious RDP server via remote desktop to gain file system access to the client machines of other connected users. Upon connecting, the malicious server could read or tamper with clipboard contents and the victim’s filesystem contents. This could lead to data privacy issues, lateral movement and privilege escalation.
Brute Force Attack:
Typically, users use weak passwords for their systems but this is not the problem. The real problem is that they use similar credentials for RDP login. This leaves such users or the organizations these users are a part of at risk. So, these weak user sign-in credentials leave the RDP connections open to brute force attacks.
RDP Mitigation:
Mitigating RDP vulnerabilities involves implementing a combination of best practices and security measures to enhance the overall security of the Remote Desktop Protocol. Here are some essential steps to mitigate RDP vulnerabilities:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) restrictions. Workers should only access the resources necessary to get their jobs done
- Enable network-level authentication (NLA) for RDP at all times
- Restrict access to the RDP port
- Monitor RDP utilization
- Enable automatic Microsoft updates
- Implement account lockout policies
- Make strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) mandatory
Single sign-on (SSO):
SSO gives companies an edge to enforce strong passwords for their employees. This also allows them to use two-factor authentication for their user logins. By backing up behind SSO weak user sign-in credentials vulnerability can be mitigated and the network can be prevented from brute force attacks.
Best possible Mitigation for vulnerabilities:
Network Level Authentication:
By enabling Network Level Authentication, your computer will first authenticate the requester before establishing a connection. Below are the steps to configure the GPO for NLA authentication for RDP:
1.Select from Administrative Tools the Group Policy Management tool:
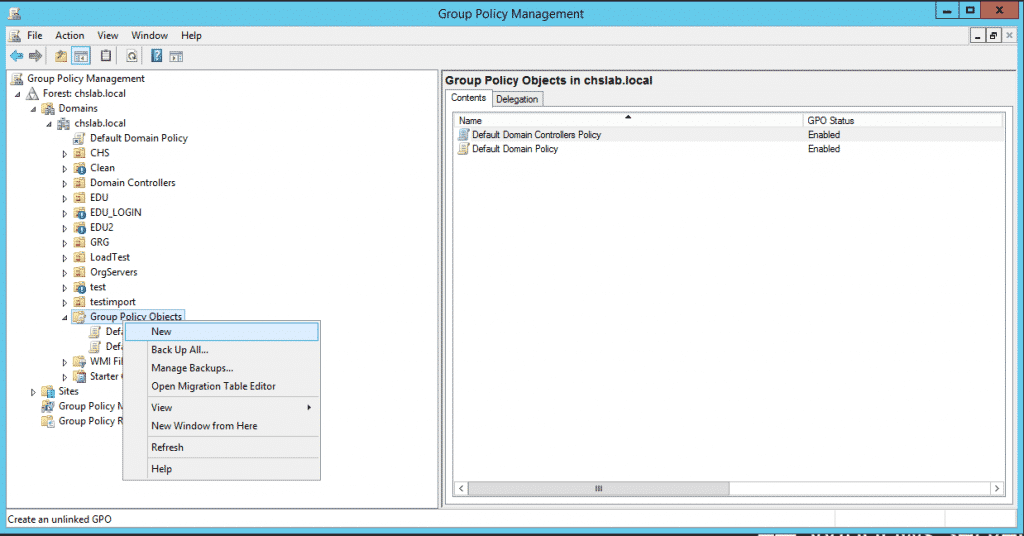
2. On the tool, create a New Group Policy Object:
3. Give this policy a Name:
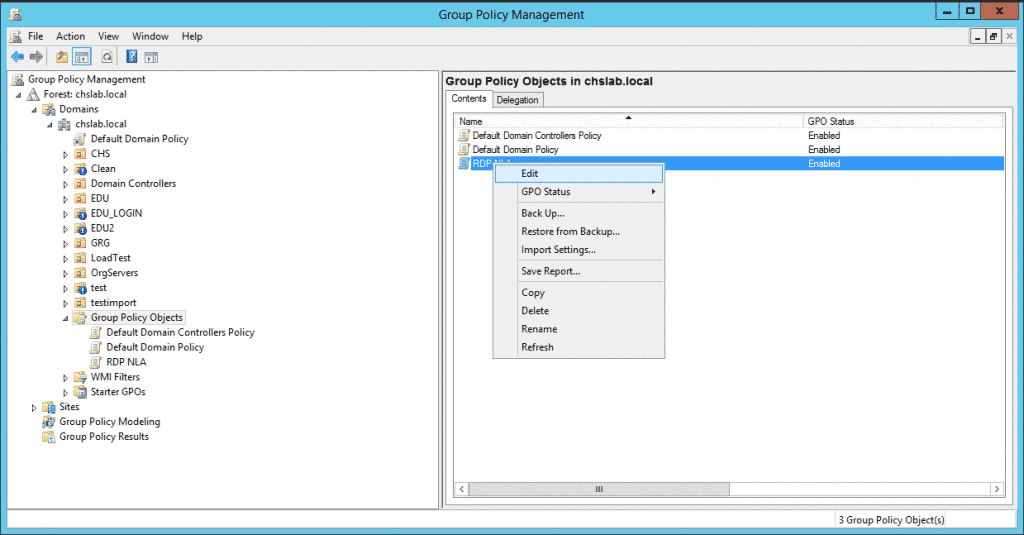
4. Edit this policy by right-clicking on it and selecting Edit:
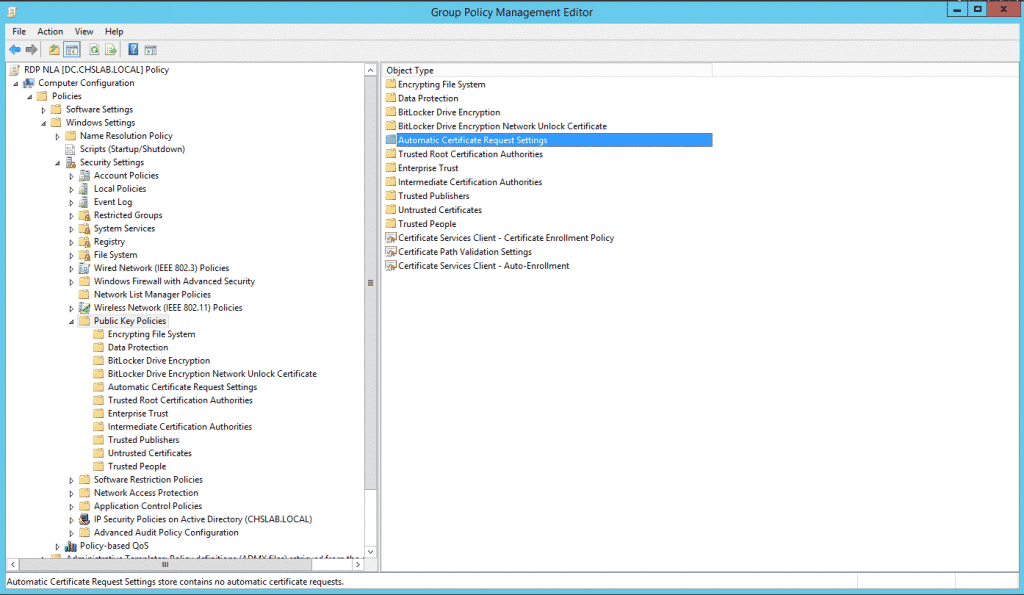
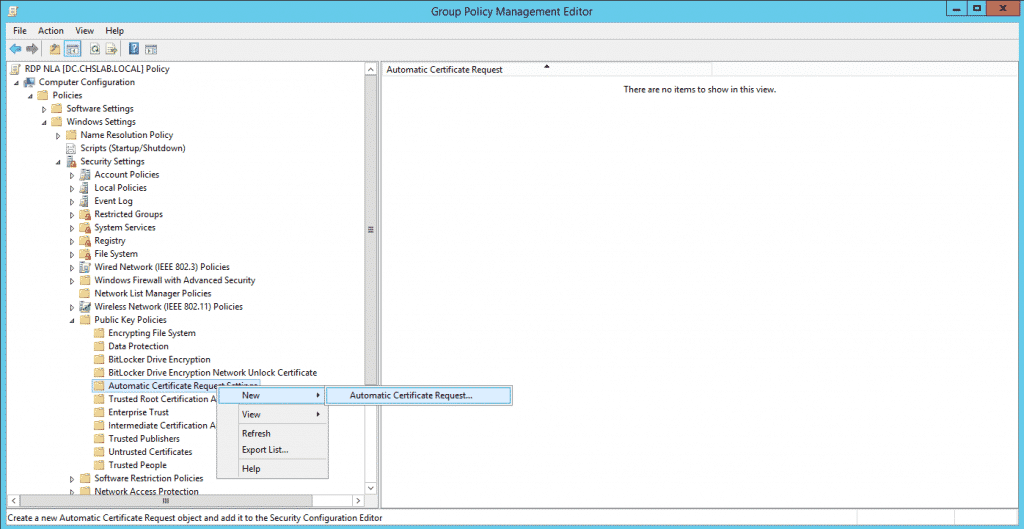
5. Select Computer Configuration/Policies/Windows Settings/Public Key Policies/Automatic Certificate Request Settings:
6. Right-click on Automatic Certificate Request Setting and select to create a new Automatic Certificate Request, this will request to the CA a new Computer Certificate and renew the certificate when it expires automatically.
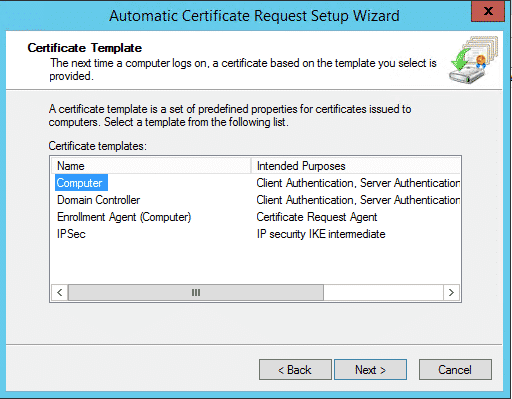
7. When the wizard starts, click Next then select Computer Certificate Template:
8. Click on Next and then on Finish. Now, select Computer Configuration/Policies/Windows Settings/Public Key Policies under that node double click on Certificate Services Client - Auto-Enrollment and select on the properties under Configuration Model select Enabled and make sure that the boxes for managing certificates in the store and for updating the certificate if the template is modified.
Now we have finished the section that will cover the certificate assignment for computers that get this GPO applied to.
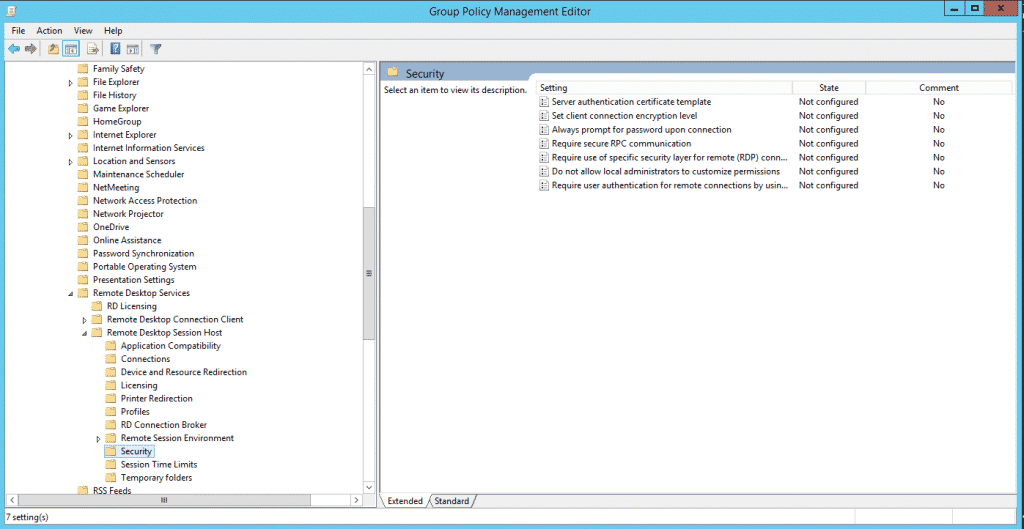
9. For configuring RDP to use NLA we now go to Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Remote Desktop Settings/Remote Desktop Session Host/Security
10. Select Require user authentication for remote connections by using Network Level Authentication and double click on it. On the properties screen select Enable and click on
Best Server hardening automation:
Hardening your systems manually is time-consuming and costly. This is attributed to the more complex nature of the network and audit requirements. CalCom offers a fully automated server hardening tool - CHS that can help with your RDP security. CHS's unique ability to 'learn' your network eliminates the need to perform lab testing while ensuring zero outages to your production environment. CHS will allow you to implement your policy directly on your production servers, hassle-free.