A study of the previous CIS Controls found that 85% of cyber incidents could be prevented by implementing only the first five controls.
2023 UPDATED CIS CONTROL ARTICLE HERE
As cyber defense evolution massively extends and faces new challenges, the industry surrounding it also extends. Moreover, selecting the right, most critical and cost-effective data security pathway is becoming a challenge of its own.
The Center of Internet Security (CIS) is a non-profit organization that gathered the proven knowledge of IT professionals to safeguard public and private organizations from cyber threats.
CIS developed a set of gold standard guidelines for organizations facing data security issues- the Critical Security Controls to simplify and help IT operations and security teams remain focused on the essentials. These activities ensure that the CIS Controls are not just another list of good things to do, but also a prioritized, highly focused set of actions with a community support network to make them implementable, usable, scalable, and compliant with all industry or government security requirements. CIS controls defense strategy is based on three key points:
- Reducing the attack surface by hardening the device configuration.
- Identifying vulnerable machines to alert long-term threats in the organization's network.
- Distributing the attackers and establishing defense and response capabilities.
According to CIS, to build an effective cybersecurity program for an enterprise, there are five critical points to consider:
- Offense informs defense: Use existing information about past attacks and how they were handled, using only methods that have been proven to work on past attacks.
- Prioritization: First, invest in Controls that will give you the highest advantage in front of the most dangerous threats that can be implemented in your system.
- Metrics: Create a common language inside your company that will be used to measure the effectiveness of the security measures, so that adjustments can be identified and implemented quickly.
- Continuous diagnostics and mitigation: Use continuous measurements to test and validate the effectiveness of the current security measures and to help drive the priority of the next steps.
- Automation: Automate defenses so organizations can achieve reliable, scalable, and continuous measurements of their adherence to the Controls and related metrics.
CIS offers twenty controls designed to help the organization secure their systems from known attack vectors. They are based on the latest information about common attacks. There are three categories of controls:
- Basic (CSC 1-6): key controls which should be implemented in every organization to achieve essential cyber defense readiness
- Foundational (CSC 7-16): these technical best practices provide clear security benefits and are a smart move for any organization to implement
- Organizational (CSC 17-20): these remaining controls have a stronger focus on the people and processes involved in cybersecurity
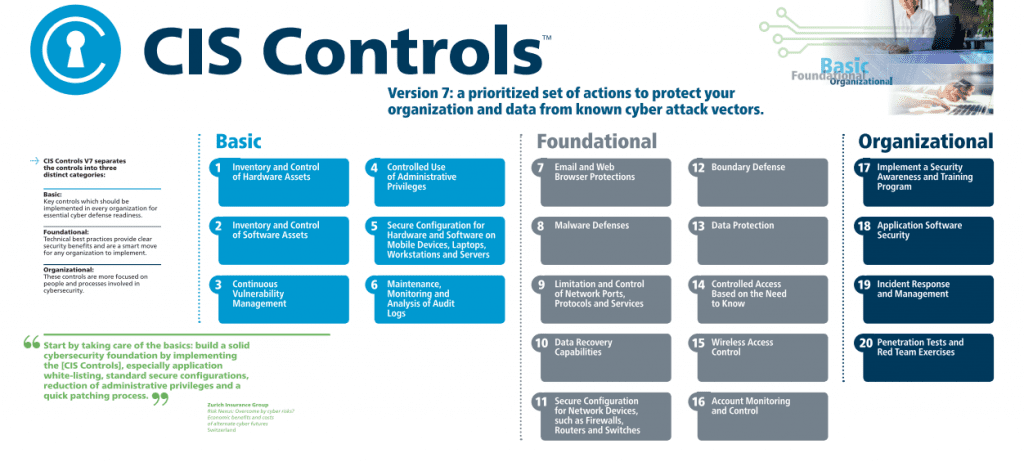
The basic CIS controls are necessary for every organization cybersecurity program, regardless of its size or industry.
Summary of six top key controls:
#1. Inventory of Authorized and Unauthorized Devices.
Main point: Organizations must actively manage all the hardware devices on the network, so only authorized devices are given access. Unauthorized and unmanaged devices need to be prevented from gaining access. If they happen to achieve access, they need to be discovered, before any damage is inflicted.
Attackers are continuously scanning the address space of organizations, waiting for new and unprotected systems to be attached to the network, and gain access using it. Moreover, this is especially relevant for enterprises that allow bringing your own device (BYOD) policy, that connects and disconnects the network, and by that can be a breach.
#2. Inventory of Authorized and Unauthorized Software.
Main point: Organizations must actively manage all software on the network, so only authorized software is installed and can execute. Security measures like application whitelisting can enable organizations to find unauthorized software and prevented installation or execution quickly.
Attackers look for vulnerable versions of software that can be exploited remotely. Therefore, having sufficient knowledge of what software has been deployed in your organization is essential for data security and privacy.
#3. Secure Configurations for Hardware and Software.
Main point: Companies need to establish, implement and manage the security configuration of laptops, servers, and workstations. Companies have to follow rigorous configuration and change control processes to prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerable services and settings.
CIS Benchmarks – What are They and How to Use Them
Manufacturers and resellers design the default configurations of operating systems and applications for ease of deployment and use. This policy often contradicts with security policies, as open services and ports, and default accounts or passwords can be exploitable in their default state. Companies invest a significant amount of energy and resources to develop configuration settings with good security properties. CIS configuration benchmarks are constantly being updated, and companies are demanded to follow them to maintain a secure system. When it comes to server infrastructures in large and complex environments, changing the server's configuration can lead to server's outage, as keeping track after services and processes dependencies are extremely complicated. This complexity often leads to either recognized or unrecognized infrastructure vulnerabilities. Another challenge that raises is deciding what will be each server's security policy, according to its role. When overcoming all of the above, another challenge is to manually implement changes. Every change will demand to overcome all the challenges all over again.
#4. Continuous Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation.
Main point: Organizations need to continuously acquire, assess and take action on new information (e.g., software updates, patches, security advisories, and threat bulletins) to identify and remediate vulnerabilities and minimize the window of opportunity for attackers
Information about new vulnerabilities updates is accessible to all. As soon as researchers report new vulnerabilities, a race starts among all relevant parties: Hackers rashes to use the vulnerability for an attack, security and IT operation teams deploy patches or updates, and defenders perform risk assessments or regression testing. Attackers can take advantage of gaps between the appearance of new knowledge and remediation.
Three important tasks will help a company have the upper hand with vulnerabilities assessment and remediation:
- Vulnerabilities Scanning- vulnerability scanner will diagnose and analyze the system's vulnerabilities. The scanner will define, identify and classify the security breaches in a computer, server, network or communication infrastructure. It can also forecast the effectiveness of security actions, and their impact on the system's functionality.
- Patching- the patch is a software update that is released when a compromised code is detected. Patches are often addressed to solve software security vulnerabilities. Patches are publicly released and can be very hard to keep track.
- Server Hardening- server hardening is probably one of the most important tasks to be handled on a server. Servers usually come from the manufacturer with the default configuration, oriented to usability rather than security. A company must establish a solid and updated server hardening policy, with minimum security practices that rely on the staff, to protect its servers.
The Cybersecurity industry offers good tools to handle each task. It is important that those tools will be used as part of the cybersecurity program in the company so that the security process will be automated, with minimum reliance on manual labor.
The Complete System Hardening Guide
#5. Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges.
Main point: This control requires companies to use automated tools to monitor user behavior and keep track of assignments, and configuration of administrative privileges on computers, networks, and applications.
Using administrative privileges is a common method for attackers to spread inside the enterprise’s network. Gaining admin access to the network could be achieved by phishing techniques, crack or guess the password for an administrative user, or elevate the privileges of a normal user account into an administrative account. If organizations do not have resources to monitor what is going on in their IT environments, it is easier for attackers to sneak in and gain control of the system without being noticed.

The basic CIS controls are necessary for every organization cybersecurity program, regardless of its size or industry.
#6. Maintenance, Monitoring, and Analysis of Audit Logs.
Server Hardening Steps and Guide to Secure Your Server
Main point: Organizations need to collect, manage and analyze audit logs to use in the investigation and recovery process of an attack.
Lack of security logging and analysis enables attackers to hide their location and activities in the network. Even after it has been revealed which systems have been compromised, without complete logging records, it will be difficult to measure the damage extent and remediate the vulnerability.
Investing energy and recourses in applying the first six CIS controls should be your main focus when building a cybersecurity program for your organization. However, it is easier said than done. Although they consider basic demand, applying and maintaining that CIS controls is a complicated mission. Due to their complexity, enterprise security and IT operation teams are often intendedly or unintendedly do not follow them, and that can be a real pain in an enterprise’s cybersecurity abilities. New cybersecurity product's main focus is automating as many security actions as can and reducing manual labor needed. Investing in getting tools that will help to execute those CIS controls can make the difference between an easy to hack and a well-defended system.
Check out how CalCom hardening automation product can be a game changer in applying the six CIS controls in your enterprise.
References:
https://blog.netwrix.com/2021/11/03/understanding-the-basic-cis-controls-csc-1-6/
https://blog.netwrix.com/2018/02/01/top-20-critical-security-controls-for-effective-cyber-defense/
https://www.sans.org/security-resources/posters/security-leadership-cis-controls/55/download
https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/vulnerability-assessment-vulnerability-analysis
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24537/patch
http://www.serverhardening.com/



