NTLM is Microsoft's old mythological authentication protocol. Although new and better authentication protocol has already been developed, NTLM is still very much in use. Basically, even the most recent Windows versions support NTLM and even Active Directory is required for default NTLM implementation. NTLM protocol has proven to have many flaws that result in potential vulnerabilities. Our main conclusion from this situation is that the best way to protect your organization from NTLM vulnerabilities is in fact, not to use it!
Although this may be the ideal situation, it is far from reality. One caution measure that can be taken is auditing and logging any NTLM traffic events, which is a fundamental step in a hardening project. Hardening can be a painful procedure when done in complex environments. If you are reading this article, you probably know it. Endless hours and resources are invested in this task. However, despite the efforts, hardening often causes downtime. In fact, over 60% of IT professionals report they've experienced downtime while trying to harden their infrastructure*.
After years of hardening using the traditional manual tools, we concluded that using hardening automation tools is essential for achieving a successful hardening project and a good compliance posture. Learn more about server hardening automation.
This post aims to provide basic information and configuration recommendations for setting NTLM Audit rules. After deciding your policy, make sure to test it before enforcing it, to make sure it will not cause damage.
This Policy Expert post will cover:
- Audit NTLM policy description.
- The potential vulnerability if not auditing.
- Countermeasures.
- The potential impact of this policy.
- Vulnerability severity.
- Setting default value.
- CalCom’s recommended value.
- How to change this setting.
POLICY DESCRIPTION:
This policy setting allows you to audit incoming NTLM traffic.
This policy is supported on at least Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2.
Note: Audit events are recorded on this computer in the “Operational” Log located under the Applications and Services Log/Microsoft/Windows/NTLM.
POTENTIAL VULNERABILITY:
NTLM is a Microsoft-developed authentication protocol that uses a challenge-response mechanism for authentication, in which client computers can prove their identities without sending a password to the server. The protocol employs three types of messages to negotiate the request, challenge the authenticity of the sender, and perform the authentication. Kerberos is a more robust protocol and is the preferred method of authentication when available.
COUNTERMEASURES:
When you need to audit NTLM use configure Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Audit Incoming NTLM Traffic to “Enable auditing for domain accounts” or “Enable auditing for all accounts” as appropriate for your environment.
POTENTIAL IMPACT:
If you select “Disable”, or do not configure this policy setting, the server will not log events for incoming NTLM traffic.
If you select “Enable auditing for domain accounts”, the server will log events for NTLM pass-through authentication requests that would be blocked when the “Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic” policy setting is set to the “Deny all domain accounts” option.
If you select “Enable auditing for all accounts”, the server will log events for all NTLM authentication requests that would be blocked when the “Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic” policy setting is set to the “Deny all accounts” option.
SEVERITY:
Critical
DEFAULT VALUE:
Not Defined.
CALCOM'S RECOMMENDED VALUE:
Enable auditing for all accounts
HOW TO CONFIGURE THE SECURITY EVENT LOG:
1. Login to the Domain Controller box.
2. Open a command-line prompt and type in:
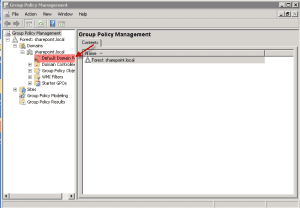
3. Now you should see the Group Policy Management screen open up. See Screenshot. Expand the Forest>Domains until you get to the “Default Domain Policy”.
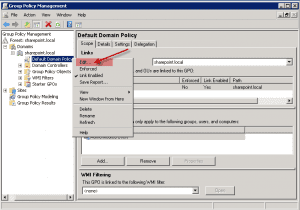
4. Highlight the “Default Domain Policy” and right-click on the mouse button. Then click on “Edit”.
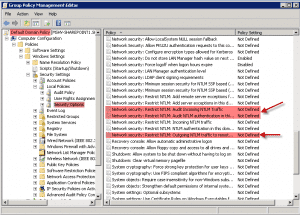
5. Now you should have the Group Policy Management Editor screen open for the Default Domain Policy. Now drill down to the Security Options (See screenshot) and then on the right scroll to what is highlighted in red with red arrows.
6. Now change the Policy Setting for the three that are highlighted in red in the above screenshot to look like this.
Network security: Restrict NTLM: Audit Incoming Traffic = Enable auditing for all accounts
*according to research done by CalCom