Do not allow COM port redirection in RDP is the name of a security setting stated in Windows servers CIS benchmarks/STIGs. A COM port is an I/O interface that enables the connection of a serial device to a computer. In some cases COM ports are called “serial ports”. Most computers are not equipped with COM ports anymore but there are many serial port devices still used in computer networks. The COM port can refer not only to physical ports but also to emulated ports, such as ports created by Bluetooth or USB-to-serial adapters.
This blog post will demonstrate:
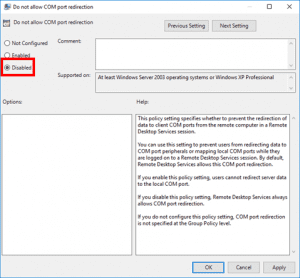
- COM port redirection policy description.
- COM port potential vulnerability.
- How to mitigate COM port vulnerability.
- The potential impact of changing this setting on your production.
- COM port redirection recommended value.
- How to change COM port settings.
POLICY DESCRIPTION:
This server hardening policy setting will determine whether the redirection of data to client COM ports from the remote computer will be allowed in the RDP session. By default, RDP allows COM port redirection. It can be used, for example, to use a USB dongle in an RDS session.
POTENTIAL VULNERABILITY:
When not enabled, users can redirect data to COM port peripherals or map the local COM ports while using the Remote Desktop Service session.
As stated by MITRE ATT&CK port redirection can lead to protocol tunneling- Adversaries may tunnel network communication to and from a victim system within a seperate protocol to avoid detection/network filtering and/or enable access to otherwise unreachable systems. Tunneling involves
explicitly encapsulating a protocol within another. This behavior may conceal malicious traffic by blending in with existing traffic and/or provide an outer layer of encryption (similar to a VPN). Tunneling could also enable routing of network packets that would otherwise not reach their intended destination, such as SMB, RDP, or other traffic that would be filtered by network appliances or not routed over the Internet. T-1572
COUNTERMEASURES:
Enable this object wherever's possible.
If the status is set to Disabled, Remote Desktop Services always allows COM port redirection. If the status is set to Not Configured, COM port redirection is not specified at the Group Policy level. However, an administrator can still disable COM port redirection using the Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration tool.
POTENTIAL IMPACT:
RDP users won't be able to access a client's COM port peripherals such as USB dongles and Bluetooth.
CALCOM'S RECOMMENDED VALUE:
Enable
HOW TO CONFIGURE RDP Do not allow COM port redirection:
1. Press Windows Logo+R, type gpedit.msc, and press Enter.
2. Click the arrow next to Computer Configuration under Local Computer Policy to expand it.
3. Click the arrow next to Administrative Templates to expand it.
4. Click All Settings to show all group policy settings.
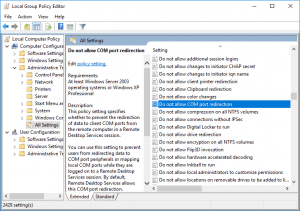
5. Scroll down to Do not allow COM port redirection and double-click on it to view the setting.
6. Ensure the policy isn’t Disabled and click OK. (Enabled must be selected).
CalCom hardening solution is a hardening automation tool designed to help IT infrastructure teams automate hardening procedure. CalCom’s solution can detect if any port redirection is required for RDP session and indicate if the setting should be enabled or not.